Operational Risk Management Establishes Which of the Following Factors
That is the people who operated the processes and equipment. Every endeavor entails some risk even processes that are highly optimized will generate risks.
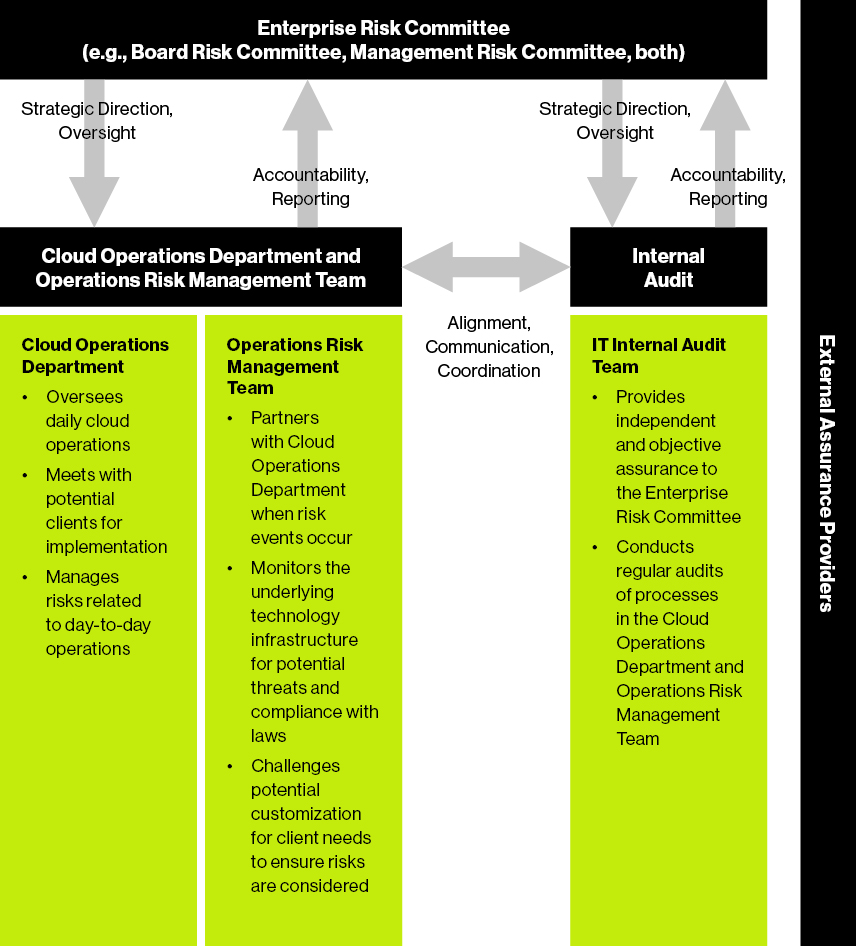
Three Lines Of Defense A New Principles Based Approach Guidehouse
Layered on top are technology riskswhich are compounded as organizations embrace new technologies like automation.

. Mark Opausky at BPS describes a scenario that highlights the dangers operational risk can pose in his article Risk Management From Your Desktop. 1 Create and Protect Value. Factors considered in the policy.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Some areas of an operational risk management capability to be developed include. What is Operational Risk Management.
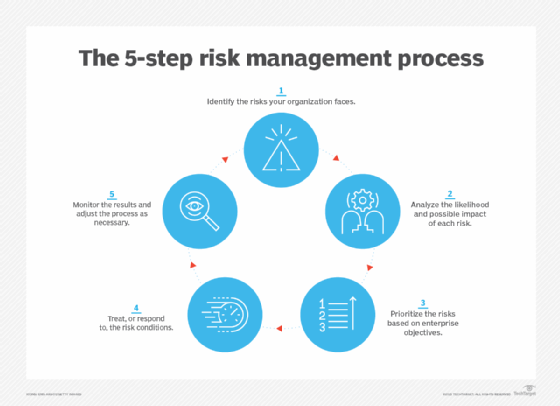
Putting governance in place over the management of risk. Risk identification risk analysis risk mitigation and risk monitoring. When looking at operational risk management it is important to align it with the.
Making informed risk decisions is the third step of the ORM process. Clearly identified senior management to support own and lead on risk. Develop controls and make risk decisions.
Accept risks only when benefits outweigh cost. Risk management cannot be done in isolation and is fundamentally communicative and consultative. Organizations in industries face operational risk wherever they turn.
Identifying operational risk is just half the journey. Damage to or loss of equipment or property. As such operational risk captures business continuity plans environmental risk crisis management process systems and operations risk people related risks and health and safety and information technology risks.
2013 the operational risk management involves the following steps. Critical success factors in risk management are. Which one of the following Risk Management is true.
Mistakes or failures due to actions or decisions made by a companys employees. BAMCIS and ORM. Identify operational risk management strategies.
The Risk Management Association defines operational risk as the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes people and systems or from external events but is better viewed as the risk arising from the execution of an institutions business functions Given this viewpoint the scope of operational risk management will encompass. ORM is a continuous systematic process of identif ying and controlling hazards to increase the certainty of outcomes. Which risk management level refers to situations when time is not a limiting and the right answer is required for a successful mission or task.
A type of business risk operational risk is distinct from. Make risk decisions at the right level. Operational Risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes people and systems or from external events but is better viewed as the risk arising from the execution of an Organizations business functions Basel Committee on Banking Supervision 2004.
Start studying Operational Risk Management ORM. In this example a hedging strategy sold by a. 3 Part of decision making.
The specific tools used to identify and assessanalyse operational risk will depend on a range of relevant factors particularly the nature including business model size complexity and risk profile of the FRFI. According to global regulatory authorities operational risk is generally defined as the risk of loss due to failed or inadequate internal processes systems people and external events the definition includes legal and compliance risk but excludes strategic and reputational risks. To better mitigate operational risks in an organization three key actions are necessary.
Which risk management model establishes a structure for. Operational risk is heavily dependent on the human factor. As defined in the Basel II text operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes people and systems or from external events.
The Basel Committee defines the operational risk as the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes people and systems or from external events. 4 Inclusive and flexible approach. A programmatic enterprise-wide operational risk management framework commonly includes components that can be tailored to specific risk areas.
This also represents the basic definition for the measurement. Steps of Risk Management. The following are a few examples of operational risk.
B130786 Operational Risk Management Operational Risk Management ORM Principles Continued PRINCIPLES OF ORM Accept no unnecessary risk. 2 Integral parts of Organizational process. To the left lie ever-present risks from employee conduct third parties data business processes and controls.
Many factors can influence operational risk. With firms operational risks include system errors human errors improper management quality issues and other operation related errors. Once the severity of the risk has been established one or more of the following.
The most common cause of task degradation or mission failure is human error specifically the inability to consistently manage risk. Operational risk can also result from a break down of processes or the management of exceptions that arent handled by standard processes. All of these risks need to be managed and the more sophisticated the approach to risk management the more chance the business has to thrive.
Every firm or individual has to deal with such an operational risk in completing any taskdelivery. This process includes detecting hazards assessing risks implementing controls and monitoring risk controls to support effective risk-based decision making. As MFIs decentralize and offer a wider range of financial products and alternative delivery channels the operational risks multiply and it becomes increasingly.
Understanding and assessing the sources of risk. ORM 5-Step Process BAMCISMETT-T. In the case of individuals we can drill it down to error because of self-process or other technical problems.
Condition with the potential to cause injury illness or death of personnel. Operational risk is the risk of financial losses and negative social performance related to failed people processes and systems in an MFIs daily operations. This definition includes human error fraud and malice failures of information systems problems related to personnel management commercial disputes accidents fires floods.
To the right are inherent cultural moral and ethical risks. One of the most important is one that can be overlooked in the concentration and the glamor of building and designing process and systems. The management of employee and contractor behavior can become a major source of operational risk.
Operational Risk Managment Risk is inherent in all tasks training missions operations and in personal activities no matter how routine. Operational risk exists in every organization regardless of size or. Anticipate and manage risk by planning.

What Is Risk Management In Healthcare
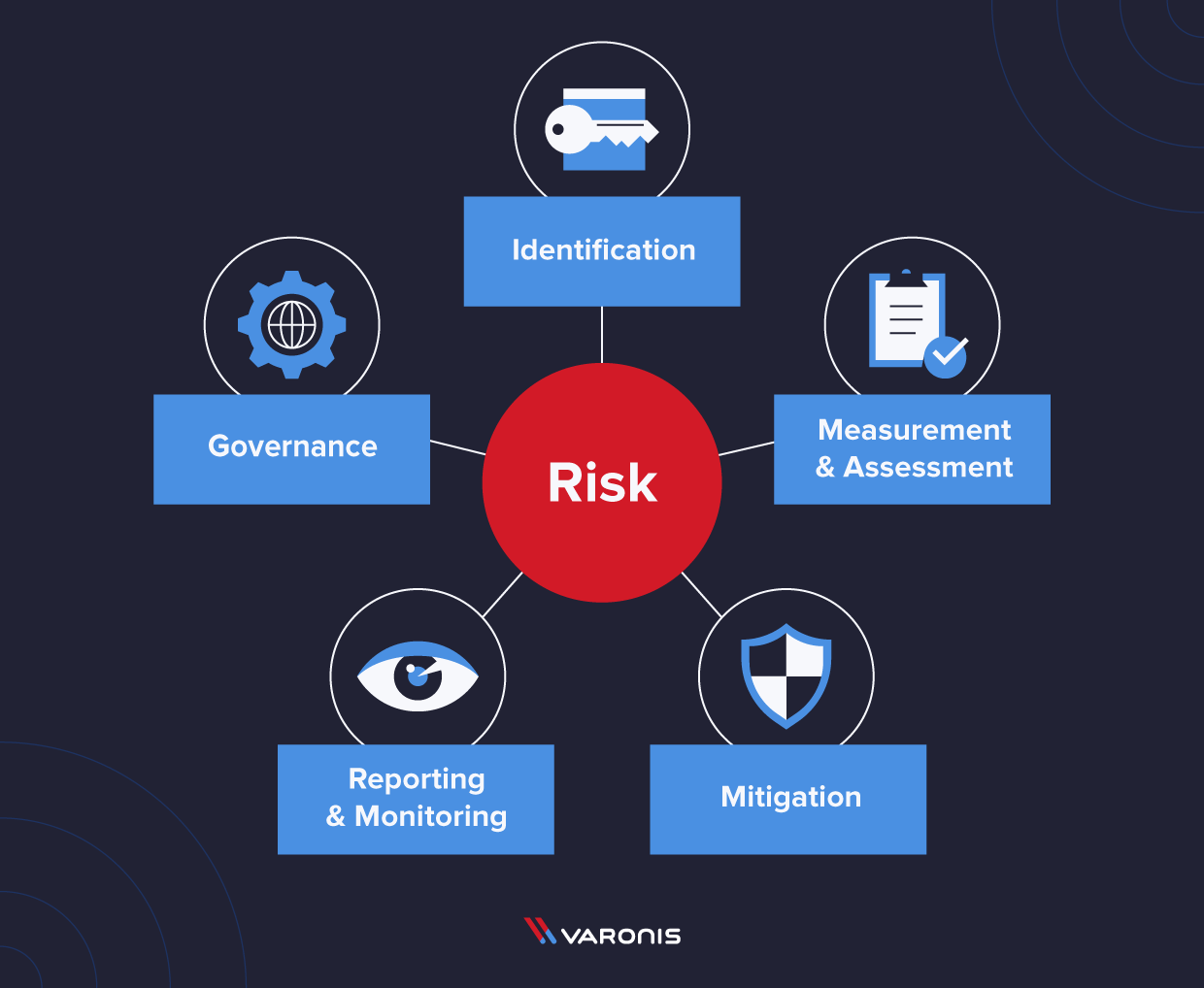
Risk Management Framework Rmf An Overview

Comments
Post a Comment